Marcellus shale
From Wikimarcellus
| Revision as of 00:32, 6 October 2008 Tcopley (Talk | contribs) ← Previous diff |
Current revision Tcopley (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | Here is where some info about the Marcellus shale formation should go. | + | The '''Marcellus shale''' formation is a marine-sedimentary, rich-organic layer of black-shale rock. It is found deep underground in an area covering approximately 65,000 square miles and stretching roughly 600 miles from southwestern [[New York]] to [[West Virginia]] and includes parts of Maryland, Kentucky, [[Ohio]] and Virginia. It is very high-quality source rock. The thickest portion of it is located in northeastern [[Pennsylvania]] and south central [[New York]] with a thickness of up to 250 feet or more. The main area of the formation is around 18 million acres. It is named for an outcropping near Marcellus, N.Y. |
| - | This article is still a stub and needs your attention. It does | + | |
| - | not have a template and contains minimal information. Please dive | + | |
| - | in and help it grow! | + | |
| - | The '''Marcellus shale''' formation is a marine sedimentary layer of black shale rock found deep underground in an area stretching roughly 600 miles from southwestern [[New York]] to West Virginia and includes parts of Maryland, Kentucky, Ohio and Virginia. The thickest portion of the formation is located in [[Pennsylvania]]. It is named for an outcropping near Marcellus, N.Y. The gas is found in pores in the rock formation so tight that gas is released very slowly or the gas tightly adheres to the rock. Both conditions may be true. | + | Gas in the formation is found trapped in natural pores and fractures of the rock so tight that it is released only very slowly or else the gas tightly adheres to the rock. Both conditions may be true. It has been accumulating in the shale due to breakdown of high levels of organic carbon or kerogen. Temperature, high pressure and time are all factors in its development. |
| - | It has been known for decades that this layer contained gas, but until recently it was not believed economical to extract. Recent improvements in technology such as [[horizontal drilling]] and [[hydro-fracturing|hydraulic fracturing]] of the shale have changed the economics somewhat. When these developments are combined with recent comparatively high prices of natural gas, it makes the endeavor profitable for all of the participants. | + | [[Image:Marcel.JPG|right|frame|<div align="center">'''Map showing extent of the Marcellus shale formation'''<br>Map courtesy of [http://www.rigzone.com/ Rigzone]</div>]] |
| - | Recent estimates indicate that there are 50 trillion cubic feet of recoverable natural gas in the Marcellus shale. This is twice the amount consumed during 2007 in the U.S. | + | The Marcellus shale has three main sub-divisions: |
| - | [[Pennsylvania]] has around one half of the proven U.S. natural gas reserves. The proximity of most of the deposits to the natural gas consuming cities of the east coast make the Marcellus an especially attractive target for exploration. | + | * Cherry Valley Limestone (differently named in various locations) |
| + | * Oatka Creek Shale | ||
| + | * Union Springs Shale | ||
| - | The Marcellus shale formation is usually found at a depth of 5,000 to 8,000 feet, but can run as deep as 9,000 feet. | + | These layers of rock have different organic contents as well as their own separate thickness characteristics due to the way in which the shale was originally deposited and over time eroded. |
| + | |||
| + | It has been known for decades that this layer contained natural gas, but until recently it was not believed economical to extract. Recent improvements in technology such as [[horizontal drilling]] and [[hydro-fracturing|hydraulic fracturing]] of the shale have somewhat changed its [[drilling economics|economics]]. When these developments were combined with the comparatively high prices of natural gas during the first half of 2008 this endeavor appeared profitable for all of its participants. Earning a reasonable return on investment may now prove more elusive since natural gas prices dipped under US $8 per Mmbtu for most of the second half of 2008, and were under $5 for much of 2009 and the first half of 2010. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Recent estimates have ranged from between 50 and 500 trillion cubic feet (Tcf) of natural gas that could be produced from Marcellus shale. As more and more favorable drilling results become available to benchmark estimates, forecasters have grown increasingly confident about making projections closer to the high end of this range. 500 Tcf would be enough gas to supply the entire U.S. for about twenty years at the present rate of consumption. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In some [[Wet gas region|areas]] of the formation, [[Natural gas liquids|natural gas fractions]] are also present such as butane, [[ethane]], and propane. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Pennsylvania]] has around one half of the proven U.S. natural gas reserves. The proximity of most of the deposits to the natural gas consuming cities of the east coast makes the Marcellus an especially attractive target for exploration. Roughly 90% of the 5,000 Marcellus wells drilled between 2007 and 2012 in Pennsylvania have been in only 11 of the state's 67 counties. Most of the drilling has either been in the northeastern ones or else those in the southwestern part of the state. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Marcellus shale formation is usually found at a depth of 5,000 to 8,000 feet, but can run as deep as 9,000 feet. Pressure gradients range between .40 to .58 psi. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!-- [[Image:Washington_co_rig_sm.gif|left|frame|<div align="center">'''Drilling rig in rural Washington Co., PA'''<br>Photo credit - [http://donnan.com/ donnan.com]</div>]] --> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Marcellus shale drilling rigs are roughly twice the size of ones used for shallow wells. They are usually around 150 feet high, with an equipment platform 20 feet off the ground. Horizontal drilling rigs are bigger still requiring larger horsepower engines to drive the drill bits further along. | ||
| The production of a typical shale gas well drops off significantly after the initial year or two and then slowly declines after that over its full lifetime. | The production of a typical shale gas well drops off significantly after the initial year or two and then slowly declines after that over its full lifetime. | ||
| Line 19: | Line 32: | ||
| One method of prospecting for gas, not only in shale formations but also for gas found within deeper structures below, is to use [[seismic waves]] to map out the underground location of deposits. | One method of prospecting for gas, not only in shale formations but also for gas found within deeper structures below, is to use [[seismic waves]] to map out the underground location of deposits. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Exploration typically begins with vertical wells. If natural gas is found in commercial quantities and grade then the initial production can help fund later horizontal drilling. | ||
| + | |||
| + | When gas shows are spotted in traditional source rocks then it merits further investigation. This may consist of reviewing existing data from the well, examining core samples and analyzing other information. | ||
| + | |||
| + | If the results of the preliminary investigation look promising then vertical wells are drilled to locate the most prospective part of the formation and confirm the characteristics of the reservoir. Analysis of [[seismic data]] also plays a role. | ||
| + | |||
| + | If all looks good, then horizontal drilling may be undertaken. | ||
| + | |||
| + | A horizontal well bore has the benefit of intersecting more of the shale and producing far greater amounts gas once it is [[hydro-fracturing|hydro-fractured]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Companies operating in the Marcellus shale area have generally benefited from improved drilling and completion techniques as they have gained more experience in the play. They have been targeting the more brittle parts of the shale formation that provide the richest organic material. These are the best places to [[Hydro-fracturing|frac]]. As [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Experience_curve_effects learning curve economics] begins to work more in the drilling companies favor, it has opened up a greater range of geography for development as the drillers have gained greater confidence in their operations. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Resources ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Marcellus_shale -Wikipedia.org on ''Marcellus Formation'']<br> | ||
| + | [http://www.api.org/policy/exploration/hydraulicfracturing/hydraulicfracturing.cfm -American Petroleum Institute video on ''Horizontal drilling And Hydraulic Fracturing''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Geological Formation]] | ||
Current revision
The Marcellus shale formation is a marine-sedimentary, rich-organic layer of black-shale rock. It is found deep underground in an area covering approximately 65,000 square miles and stretching roughly 600 miles from southwestern New York to West Virginia and includes parts of Maryland, Kentucky, Ohio and Virginia. It is very high-quality source rock. The thickest portion of it is located in northeastern Pennsylvania and south central New York with a thickness of up to 250 feet or more. The main area of the formation is around 18 million acres. It is named for an outcropping near Marcellus, N.Y.
Gas in the formation is found trapped in natural pores and fractures of the rock so tight that it is released only very slowly or else the gas tightly adheres to the rock. Both conditions may be true. It has been accumulating in the shale due to breakdown of high levels of organic carbon or kerogen. Temperature, high pressure and time are all factors in its development.
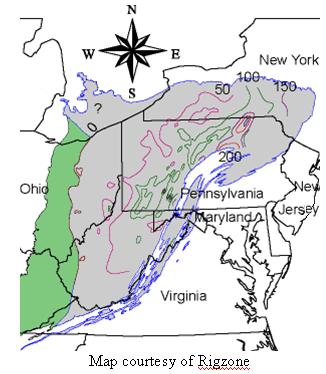
Map courtesy of Rigzone
The Marcellus shale has three main sub-divisions:
- Cherry Valley Limestone (differently named in various locations)
- Oatka Creek Shale
- Union Springs Shale
These layers of rock have different organic contents as well as their own separate thickness characteristics due to the way in which the shale was originally deposited and over time eroded.
It has been known for decades that this layer contained natural gas, but until recently it was not believed economical to extract. Recent improvements in technology such as horizontal drilling and hydraulic fracturing of the shale have somewhat changed its economics. When these developments were combined with the comparatively high prices of natural gas during the first half of 2008 this endeavor appeared profitable for all of its participants. Earning a reasonable return on investment may now prove more elusive since natural gas prices dipped under US $8 per Mmbtu for most of the second half of 2008, and were under $5 for much of 2009 and the first half of 2010.
Recent estimates have ranged from between 50 and 500 trillion cubic feet (Tcf) of natural gas that could be produced from Marcellus shale. As more and more favorable drilling results become available to benchmark estimates, forecasters have grown increasingly confident about making projections closer to the high end of this range. 500 Tcf would be enough gas to supply the entire U.S. for about twenty years at the present rate of consumption.
In some areas of the formation, natural gas fractions are also present such as butane, ethane, and propane.
Pennsylvania has around one half of the proven U.S. natural gas reserves. The proximity of most of the deposits to the natural gas consuming cities of the east coast makes the Marcellus an especially attractive target for exploration. Roughly 90% of the 5,000 Marcellus wells drilled between 2007 and 2012 in Pennsylvania have been in only 11 of the state's 67 counties. Most of the drilling has either been in the northeastern ones or else those in the southwestern part of the state.
The Marcellus shale formation is usually found at a depth of 5,000 to 8,000 feet, but can run as deep as 9,000 feet. Pressure gradients range between .40 to .58 psi.
Marcellus shale drilling rigs are roughly twice the size of ones used for shallow wells. They are usually around 150 feet high, with an equipment platform 20 feet off the ground. Horizontal drilling rigs are bigger still requiring larger horsepower engines to drive the drill bits further along.
The production of a typical shale gas well drops off significantly after the initial year or two and then slowly declines after that over its full lifetime.
In the industry, it is known as an “unconventional deposit.”
One method of prospecting for gas, not only in shale formations but also for gas found within deeper structures below, is to use seismic waves to map out the underground location of deposits.
Exploration typically begins with vertical wells. If natural gas is found in commercial quantities and grade then the initial production can help fund later horizontal drilling.
When gas shows are spotted in traditional source rocks then it merits further investigation. This may consist of reviewing existing data from the well, examining core samples and analyzing other information.
If the results of the preliminary investigation look promising then vertical wells are drilled to locate the most prospective part of the formation and confirm the characteristics of the reservoir. Analysis of seismic data also plays a role.
If all looks good, then horizontal drilling may be undertaken.
A horizontal well bore has the benefit of intersecting more of the shale and producing far greater amounts gas once it is hydro-fractured.
Companies operating in the Marcellus shale area have generally benefited from improved drilling and completion techniques as they have gained more experience in the play. They have been targeting the more brittle parts of the shale formation that provide the richest organic material. These are the best places to frac. As learning curve economics begins to work more in the drilling companies favor, it has opened up a greater range of geography for development as the drillers have gained greater confidence in their operations.
Resources
-Wikipedia.org on Marcellus Formation
-American Petroleum Institute video on Horizontal drilling And Hydraulic Fracturing

